



Hyperspectral Insights for Healthier Crops and Sustainable Land Management
Hyperspectral imaging offers a powerful and non-destructive method to monitor crop health, optimize yields, and support sustainable agriculture.
By capturing detailed spectral data across hundreds of narrow, contiguous wavelengths, hyperspectral imaging reveals subtle variations in vegetation and soil that are often undetectable to the human eye and traditional RGB or multispectral systems. This detailed spectral information enables precise assessment of crop vigor, chlorophyll content, soil variability, and plant physiology throughout the growing season.
As a result, hyperspectral imaging supports advanced applications such as precision agriculture, crop classification, yield prediction, and long-term vegetation monitoring, delivering actionable insights that help optimize inputs, improve crop quality, and support data-driven farm management.

Key Benefits of Hyperspectral Imaging for Agriculture & Vegetation:
- Early Detection of Crop Stress: Identify nutrient deficiencies, disease, drought stress, and pest infestation before visual symptoms are present.
- Precision Agriculture: Optimize irrigation, fertilization, and pesticide application by mapping field variability with high spectral resolution.
- Yield Forecasting and Biomass Estimation: Estimate crop performance and predict harvests with greater accuracy using spectral indices and models.
- Vegetation Classification and Land Cover Mapping: Distinguish plant species and monitor biodiversity with fine spectral detail.
- Soil and Plant Interaction Analysis: Evaluate soil properties and plant response to environmental conditions for better informed agronomic decisions.

Precision Crop Management
Hyperspectral imaging enables a new level of precision in crop health assessment by collecting detailed spectral information that reveals subtle physiological changes in plants long before they are visible to the human eye or RGB imaging systems.
By analyzing reflectance patterns across hundreds of narrow wavelength bands, growers and agronomists can detect early signs of stress related to disease, water availability, or nutrient deficiencies. This detailed insight supports data-driven decision-making, allowing targeted interventions that improve crop performance, reduce losses, and promote more sustainable farming practices.
Within precision agriculture workflows, hyperspectral imaging plays a critical role in optimizing nutrient management and enhancing weed detection. UAV-optimized hyperspectral systems, such as the Specim AFX10 and AFX17, make it possible to map nutrient variability across a field, enabling variable-rate fertilizer application that matches inputs to actual crop needs. At the same time, hyperspectral signatures can distinguish crops from weeds with high accuracy, even when they appear visually similar, supporting site-specific weed management strategies.
The result is more efficient use of inputs, reduced chemical application, and improved yields through smarter, more precise crop management.
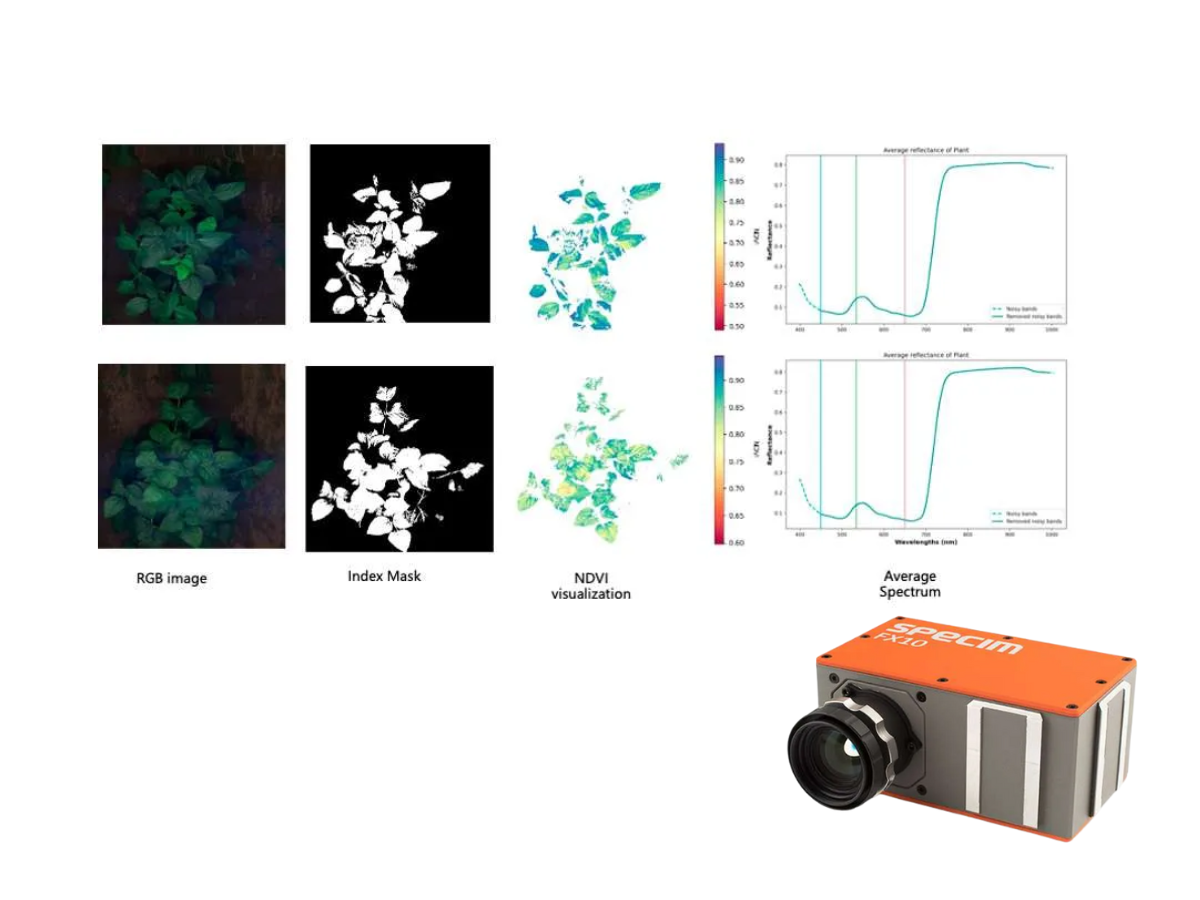
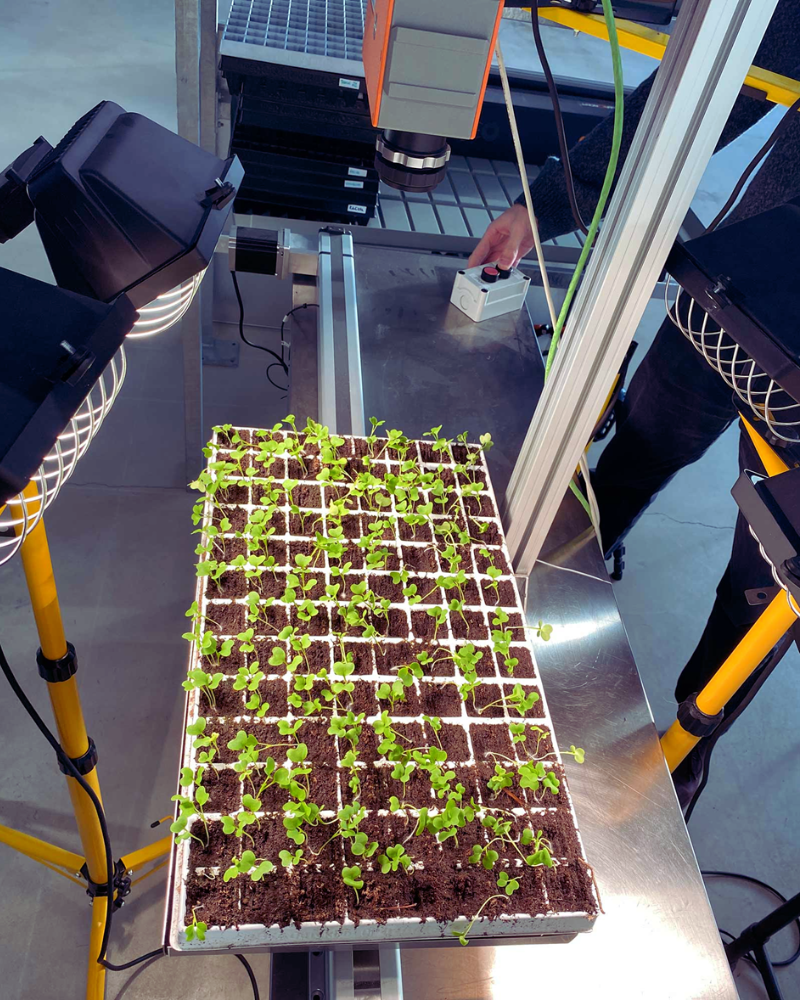
Plant Phenotyping
Plant phenotyping is essential for understanding how plants grow, adapt and respond to their environment. Hyperspectral imaging provides objective, high-throughput and non-invasive measurement of plant traits across hundreds of spectral bands.
With hyperspectral imaging technology, researchers can:
- Characterize physiological traits through subtle variations in chlorophyll content, photosynthetic activity, water status and nutrient uptake
- Monitor growth dynamics by tracking plant development, leaf area index, canopy structure and biomass accumulation over time
- Detect and identify biotic and abiotic stressors such as pathogens, drought, heat and salinity before visible symptoms present
- Accelerate breeding programs by screening large populations rapidly and objectively to identify high-performing genotypes with desirable traits
- Enable multiscale research through integration of data from leaf, canopy and field level, supporting both controlled environmental studies and large-scale agricultural trials
Through the combination of hyperspectral data with advanced analytics, machine learning and predictive models, researchers are able to gain a more comprehensive understanding of plant physiology and genetics than ever before.
Case Study: UAV Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Enables Efficient Crop Phenotyping
Case Study: Hyperspectral Imaging Meets High-Throughput Plant Phenotyping in LemnaTec Solutions
Case Study: PhenoTrait: Transformative Impact of Hyperspectral Imaging on Plant Phenotyping

Soil Composition and Moisture Analysis
Soil is the foundation of sustainable agriculture, land management and environmental stewardship. Hyperspectral imaging provides a fast, non-destructive and highly accurate method to analyze soil properties both in the lab and the field. By capturing detailed spectral signatures, hyperspectral imaging enables precise assessment of soil composition, structure and moisture content.
Key applications for hyperspectral imaging technology in soil analysis include:
- Soil composition mapping: Identifying and quantifying organic matter, minerals and nutrients for improved land use and crop planning
- Moisture monitoring: Detection and monitoring of variations in soil water content to support irrigation management and drought resilience
- Nutrient deficiency detection: Early detection of soil nutrient imbalance, helping optimize fertilizer use and reduce environmental impact
- Large-scale land assessment: Hyperspectral remote sensing to monitor soil health across farms, watersheds or entire regions
Hyperspectral imaging allows researchers, farmers and policymakers to make informed decisions that improve yield, conserve resources and protect ecosystems.
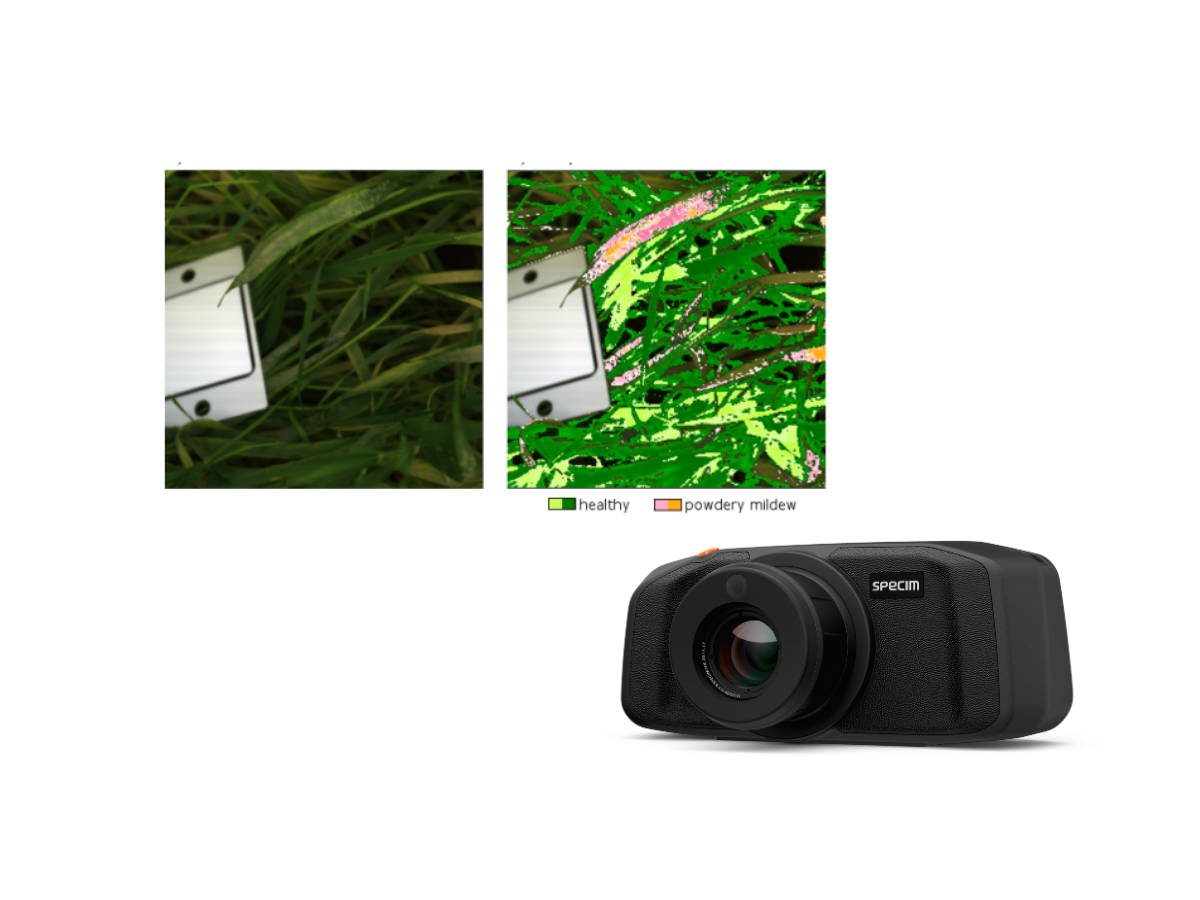

Vegetation Research
Hyperspectral imaging is a transformative tool for vegetation research, providing scientists with a non-destructive, data-rich approach to study plant structure, function, and dynamics across a wide range of environments.
Using high-quality hyperspectral imaging technology, researchers can precisely assess vegetation properties such as chlorophyll content, water status, leaf chemistry, and canopy structure. This level of spectral detail enables the detection of subtle physiological and biochemical changes that are often impossible to observe with traditional RGB or multispectral imaging methods, making hyperspectral imaging especially valuable for advancing plant science and ecological research.
Hyperspectral imaging supports both controlled laboratory studies and large-scale field investigations, bridging the gap between plant-level measurements and ecosystem-scale observations. Researchers can use hyperspectral data to investigate plant responses to environmental stressors such as drought, heat, nutrient limitation, and disease, helping to uncover underlying mechanisms of stress tolerance and adaptation. Hyperspectral technology also enables species differentiation, phenotyping, and biodiversity assessment by identifying unique spectral signatures associated with different plant types or functional traits.
When combined with advanced analytics, modeling, and machine learning, hyperspectral imaging provides actionable insights that improve our understanding of vegetation health, productivity, and resilience, supporting research in agriculture, forestry, ecology, and climate science.
